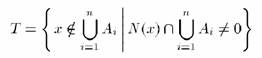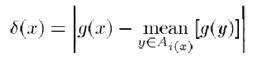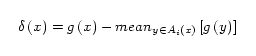�椸4. Segmentation II : Region Growing
|
1. Region-based segmentation: �p�GR���ܤ@�i�v���������d��A�v�����Ϊ��ت��O�NR���Φ�n�Ӱ϶��GR1,R2,�K,Rn �ú����U�C����G
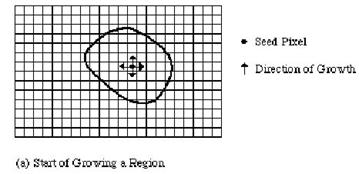
Seeded Region growing�G ����@��ؤl(seed)pixels�A�Hseed���֤߶i������(grow)�A�P�_seed�P��pixels�O�_�Pseed�㦳�ۦ����S��(�Ƕ��ȡB�`�z�B��m) �A�p�G�O�A�h������pixel���P�@region�A�A�H���s��pixel���֤ߡA�~�d�P��|���Q�k������@region��pixel�A����v���Ҧ�pixels�����������C Following Adams and
Bischof, we say that the seeds are grouped into n sets, A1; A2; . . .; An. Each step
of the algorithm adds a single pixel to one of these sets. To achieve this
and maintain a homogeneity criterion, the set T of all as-yet
unallocated pixels bordering at least one region is employed
where N(x) is the
nearest eight neighbors of the pixel x. If for x
where g(x) is the
gray-scale intensity value of x. If N(x) meets two or more of the Ai, the value i(x) is taken to
be the value of i
such
that N(x) meets Ai and d(x)
is
minimized. A z
and append z to Ai(z). This
completes a single step of the algorithm and the same process is iterated
until all pixels have been allocated to a set. The implementation of
SRG employs a linked list storing the data of T , which is ordered
according to d(x) . Adams and Bischof
refer to this as a sequentially sorted list (SSL). The SSL remains ordered
throughout the progression of the algorithm, so that by simply processing the
first entry at each time step, d(x) is
satisfied. Thus, a search cost must be incurred to locate appropriate
positions when adding new members to the SSL. �t��k�G Initialization: �@��²�ƪ��t��k�����G // main function ...... /* Initialize region statistics */ Total = Count = 0; for (y = Yseed - 5; y <= Yseed + 5; y++) for (x = Xseed - 5; x <= Xseed + 5; x++)if ((x >= 0) && (y >= 0) && (x < nc-1) && (y < nr-1)) { Count++; Total += ima1.m[y][x]; } /* Perform recursive seeded region growing */ RegionGrow(ima1, ima2, Xseed, Yseed); cout<<"region contain "<<Count<<" points with mean value = "<<Total/Count; ......
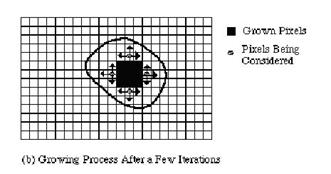
// RegionGrow function void RegionGrow(uc2D &ima1, uc2D &ima2, int x, int y){ float Diff, Mean; /* Check to see if point already part of region */ if (ima2.m[y][x] == 0) { /* See if point is close enough to add */ Mean = Total / Count; Diff = ima1.m[y][x] - Mean; if (Diff < 0) Diff = -Diff; if (Diff < Threshold) { /* Add point to region and consider neighbors */Total += ima1.m[y][x]; Count++; ima2.m[y][x] = 1;if (x > 0) RegionGrow(x - 1, y); if (y > 0) RegionGrow(x, y - 1); if (x < Xdim - 2) RegionGrow(x + 1, y); if (y < Ydim - 2) RegionGrow(x, y + 1); } }}Region Growing�ܷN��
���D�G l
Seed-dependent
: ��ܤ��Pseed�N�|�����P���v�����ε��G�F. l
�p�Gseed��n���edge�N�L�k�i��v������ ��g���n�ѦҤ��m�G
�䥦�̷s�ѦҤ��m�G Robert D. Stewart, Iris Fermin, and
Manfred Opper . Region growing with pulse-coupled
neural networks, IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NEURAL NETWORKS, VOL. 13, NO. 6,
NOVEMBER 2002 |